Oral Cavity Anatomy, Functions, and Diseases Medical Library
The alveolar bone is covered by specialized oral mucosa known as gingiva, or, more commonly, gums. The remainder of the oral cavity is covered with an oral mucous membrane. Tooth germ formation of the primary or baby teeth begins 7 to 10 weeks in utero. This is followed by enamel and dentin apposition from 4 to 6 weeks in utero.
Dental Articles and Resources
. The teeth are hard, calcified structures used for sound articulation as well as biting and masticating food. The oral cavity is separated from the nasal cavity by the palate , which is divided into the soft and the hard palate . The masticatory movements of the jaw are enabled by the muscles of mastication

What is the Oral Cavity
Dental Care Package at Parramatta Medical and Dental Centre. Get Exclusive Deals With Groupon. Limited Time Offer
Anatomy of the Oral Cavity YouTube
The oral cavity, better known as the mouth, is the start of the alimentary canal. It has three major functions: Digestion - receives food, preparing it for digestion in the stomach and small intestine. Communication - modifies the sound produced in the larynx to create a range of sounds.

Structure Of Oral Cavity Human Mouth Anatomy Stock Vector Images and
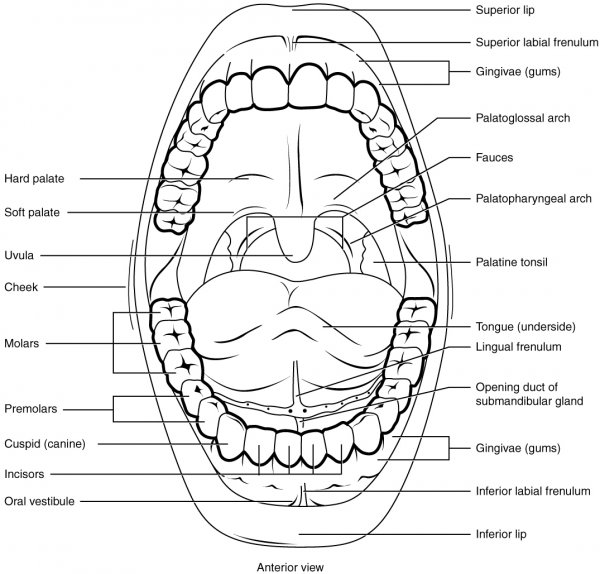
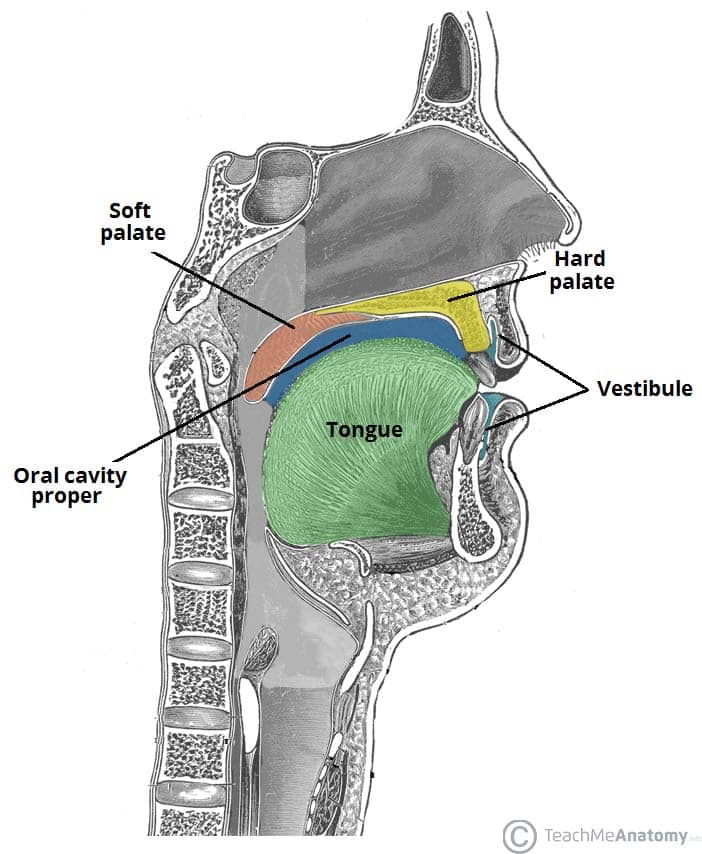
1/2 Synonyms: none The cavity is separated into anterior and posterior parts by the dental arches (or teeth): the anterior oral vestibule sits anteriorly to the teeth and behind the lips, whilst the oral cavity proper describes the area behind the teeth.
What Are the 3 Key Functions of the Teeth? Vancouver Centre for
Many parts make up your mouth anatomy. These parts work together harmoniously to help with chewing, speaking and breathing. The outside of your mouth creates a boundary that holds food in place and helps you form sounds and words. It includes your cheeks and lips. The inside of your mouth contains your: Teeth. Gums.

Schematic drawing of the oral cavity [97]. Download Scientific Diagram
A mucous membrane known as the oral mucosa is composed of stratified squamous epithelium and forms the inner lining of the mouth. Several submandibular and sublingual salivary glands secrete viscous and mucoid fluid to lubricate and keep the oral cavity moist.

The Oral Cavity Labeling Diagram Quizlet
References: Neil S. Norton, Ph.D. and Frank H. Netter, MD, Netter's Head and Neck Anatomy for Dentistry, 2nd Edition, Elsevier Saunders, Chapter 13 Oral Cavity, Page 341 to 351. Rudolf Beer, Michael A. Baumann and Andrej M. Kielbassa, Pocket Atlas of Endodontics, 1st Edition, Thieme Flexibook, Chapter 1 Anatomy and Types of Endodontic Pathology, Normal Endodontium, Page 2 and Chapter 5.

Oral Cavity Proper
Present exceptional content with your unlimited creative subscription. Download Millions of PowerPoint Templates, Graphic Assets, Fonts, Icons & More!

Oral Cavity Anatomy Model Images Galleries With A
Oral cavity Anatomy of the mouth. Floor of the mouth with lingual frenum and sublingual fold The mouth consists of two regions: the vestibule and the oral cavity proper. The vestibule is the area between the teeth, lips and cheeks. [3]

AN3 08 Oral Cavity, Oropharynx, Swallowing StudyBlue
Print Anatomy of the Oral Cavity Figure 1. Anterior view of the A external mouth and lips and B arterial supply to the lips. Figure 2. Inferior view of the maxilla. Figure 3. Cross section of a tooth. Figure 4. Lateral cross-section showing the A innervation of the lips B and teeth and gingiva. Figure 5.
The Oral Cavity Divisions Innervation TeachMeAnatomy
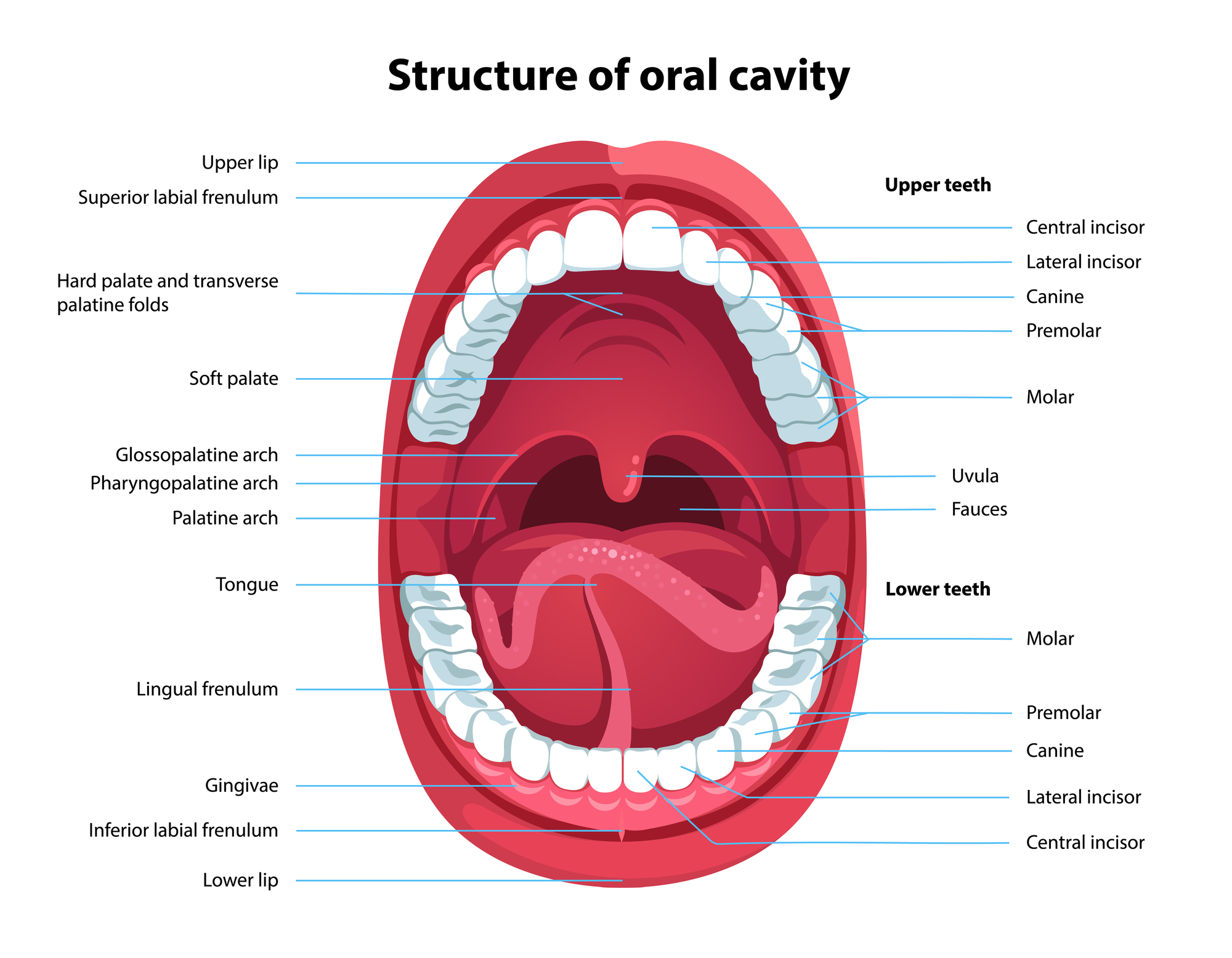
Teeth names and numbering There are thirty-two teeth in total in the oral cavity of an adult dentition. One half, or sixteen, are embedded in the maxilla, while the lower half are situated within the mandible.The name of teeth on each arcade is self-explanatory - the top sixteen are named 'maxillary teeth', while the bottom half are named 'mandibular teeth'.
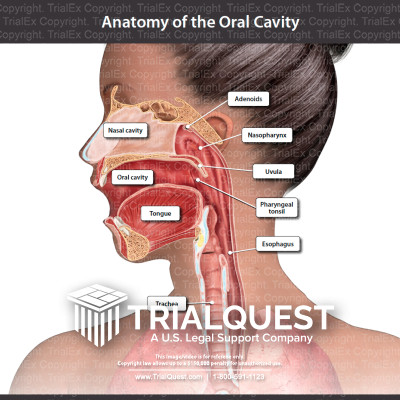
Anatomy of the Oral Cavity TrialExhibits Inc.
The roof of the oral cavity is formed by the palate, which separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity above. At the bottom, the mylohyoid muscle forms a muscular diaphragm that supports the tongue and the structures of the floor of the mouth. Finally, the lateral walls of the oral cavity are formed by the cheeks.

Oral cavity anatomy with educational labeled structure vector illustration
The anatomy of a tooth divides into two main sections: the crown and the root. The crown of the tooth is what is visible in the oral cavity, and the root of the tooth is embedded into the bony ridge of the upper and lower jaws called the alveolar process via attachment to the periodontal ligament. The gingiva covers the border of the.

Oral cavity a sagittal section showing the major components forming
Mouth conditions Where to get help Image: Dental Health Services Victoria The mouth is an oval-shaped cavity inside the skull. The two main functions of the mouth are eating and speaking. Parts of the mouth include the lips, vestibule, mouth cavity, gums, teeth, hard and soft palate, tongue and salivary glands.
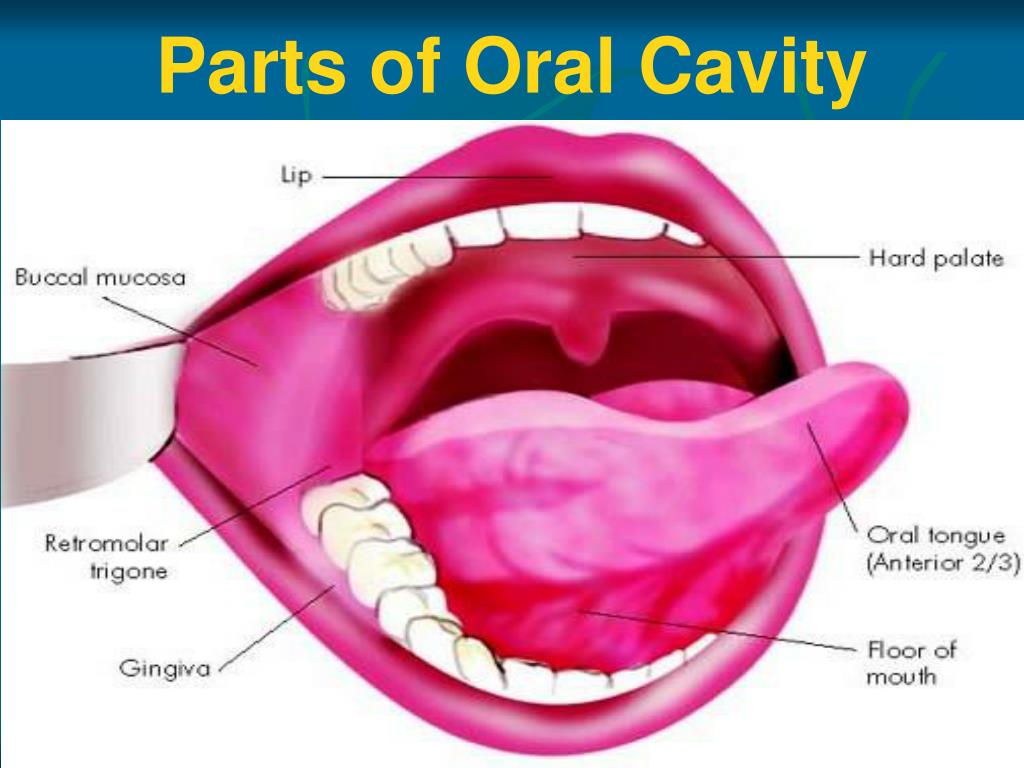
PPT Anatomy of Oral Cavity, Pharynx & Oesophagus PowerPoint
1 Citations Abstract In this section, the surface structures of the oral cavity, which is necessary to understand the mimetic muscles and floor of the mouth, will be reviewed. Download chapter PDF 3.1 Surface Anatomy of the Oral Cavity Summary